Top Five Infrared Bulb Myths
It's time to bust some myths about near infrared bulbs! Below are the five most common misconceptions our customers have about NIR bulbs / red light bulbs and the actual truth about each one.
Myth #1: Deeper red light bulbs produce more red light and near infrared energy.
Reality: Bulb color is unrelated to red infrared light production. The function of the glass portion of a lightbulb is to protect the metal filament. The filament is the portion of the bulb that produces light, heat, and near infrared energy. To learn more about this topic, review our blog post: Why Bulb Color and Performance are Unrelated.

Myth #2: Incandescent infrared bulbs have been discontinued in the United States.
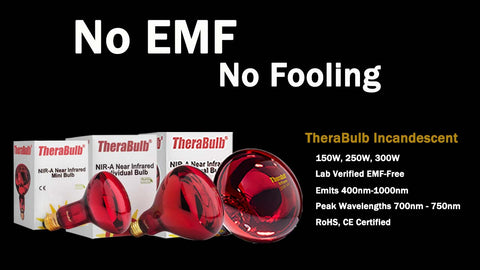
Reality: While the sale of common incandescent bulbs has been banned by the United States Department of Energy's directive, incandescent infrared bulbs such as TheraBulb's 150W heat lamp bulb, 250W heat lamp bulb, and 300W heat lamp bulb are classified as specialty bulbs and are, therefore, exempt from the ban.

Myth #3: Near infrared and infrared energy are different from one another.
Reality: Near infrared energy is infrared energy. Infrared refers to the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum from 700nm - 3000nm. Near infrared is a subset of infrared, with wavelengths from 7000nm - 1400nm. It is called near infrared because it is the portion of the infrared spectrum that is nearest to visible light (380nm - 699nm).

Myth #4: Incandescent infrared bulbs are the same as heat lamp bulbs.
Reality: Not necessarily. Incandescent infrared bulbs are a type of heat lamp or thermal bulb, but with more specific purpose. While all incandescent heat lamp bulbs produce heat, visible light (including red light), and near infrared light, the primary purpose of a heat lamp bulb is to produce heat. Incandescent infrared bulbs are designed to be used as sauna bulbs in dry saunas (also called infrared saunas) and by consumers who wish to access heat and near infrared energy for heat / light personal wellness. They are engineered to maximize red light and near infrared output. Brands like TheraBulb provide information on the energy wavelengths that the bulbs emit, their irradiance (intensity), maximum operating temperature, and other performance characteristics. In the case of TheraBulb, this data is the result of testing in an independent ISO-certified laboratory.
To learn more about the difference between heat lamp and incandescent infrared bulbs, see our blog post: How TheraBulb Near Infrared Bulbs Differ from Heat Lamp Bulbs.

Myth #5: I need a device to filter the EMF produced by my infrared incandescent bulbs.
Reality: Incandescent bulbs do not emit EMF. This is because they don't operate in a way that produces EMF. An incandescent bulb produces heat, light, and near infrared energy as the result of electricity passing through a filament. This is why TheraBulb refers to our 150W, 250W, and 300W incandescent bulbs as Zero-EMF bulbs: independent laboratory testing has confirmed that our bulbs emit no EMF.
See This Post in Video Form
Any Myths We Haven't Debunked?
Check out our Frequently Asked Questions page to learn more about near infrared and TheraBulb's products. If you still have questions or want to know if what you think you know is a myth or a fact, contact us at support@therabulbusa.com.


